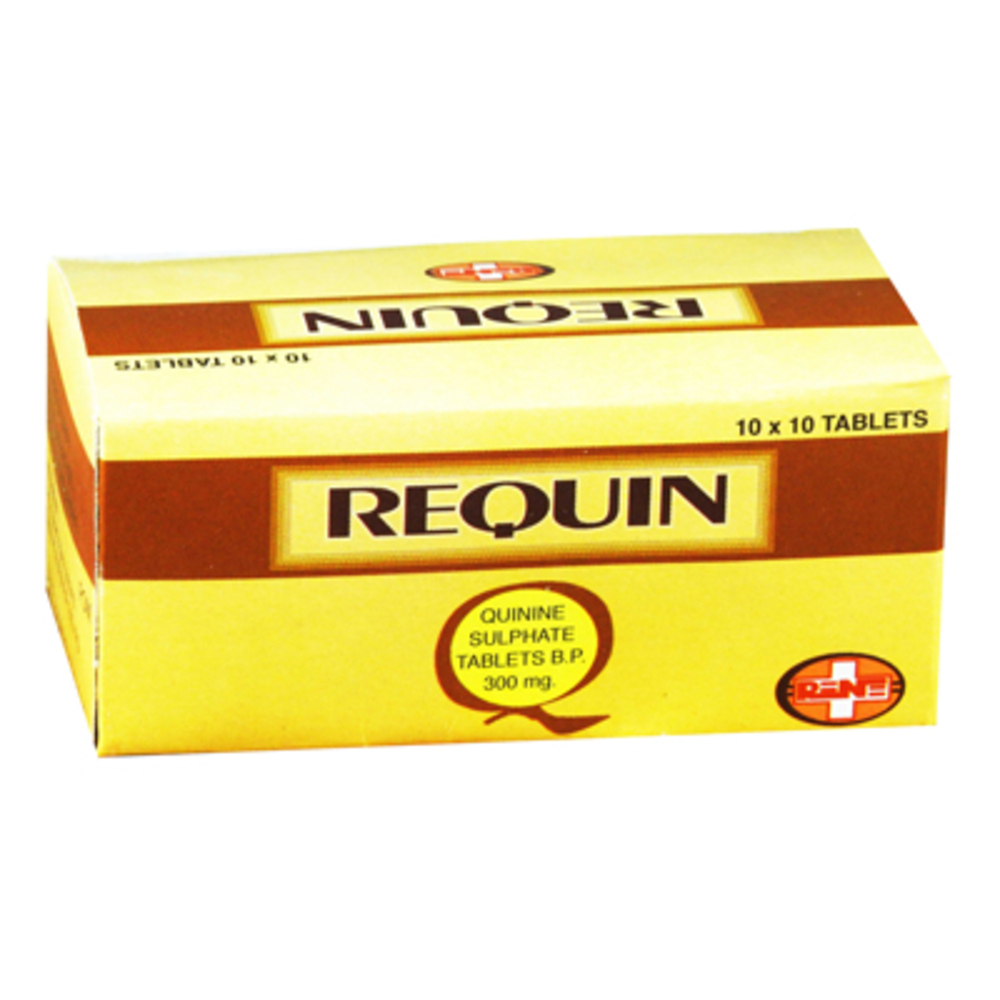
Quinine is the main alkaloid of cinchona bark. Quinine sulphate is the drug of choice in the treatment of an acute attack of falciparum malaria where the parasite is known to be resistant to chloroquine.
Presentation
Jar of 1000 Tablets
Blister pack of 10 x 10 Tablets
Indications
Treatment of Malaria: Quinine is indicated only for treatment of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Quinine sulfate has been shown to be effective in geographical regions where resistance to chloroquine has been documented.
Pharmacological class
Antiprotozoal
Pharmacological properties
Antimalarial
Mechanism of Action
Quinine inhibits nucleic acid synthesis, protein synthesis, and glycolysis in Plasmodium falciparum and can bind with haemozoin in parasitized erythrocytes. Quinine sulfate acts primarily on the blood schizont form of P.falciparum
Side effects
Quinine tablets may cause tinnitus, headache, hot and flushed skin, nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhoea and confusion, visual disturbances, rashes, hypersensitivity reactions including angioedema, blood disorders (thrombocytopenia) and acute renal failure.
Contraindications
Prolonged QT Interval: Quinine sulfate is contraindicated in patients with a prolonged QT interval. Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency: Quinine sulfate is contraindicated in patients with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G-6-PD) deficiency.
Myasthenia Gravis: Quinine sulfate is contraindicated in patients with myasthenia gravis.
Hypersensitivity: Quinine sulfate is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to quinine. Quinine sulfate is also contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to mefloquine or quinidine because cross-sensitivity to quinine has been documented.
Optic neuritis: Quinine sulfate is contraindicated in patients with optic neuritis.
Drug interactions
Antacids containing aluminium and/or magnesium may delay or decrease absorption of quinine. Concomitant administration of these antacids with quinine should be avoided.
Erythromycin was shown to inhibit the metabolism of quinine in vitro using human liver microsomes. Therefore, concomitant administration of erythromycin with quinine sulfate is likely to increase plasma quinine concentrations, and should be avoided.